Skin Cancer vs. Age Spots: How to Tell the Difference and When to Seek Help

As the largest organ of the body, your skin deserves extra special attention and care. While age spots and skin cancer may share some visual similarities, it's important to recognize the key differences between the two and know when to seek help from a professional. Fall Creek Skin and Health Clinic is here to guide you through understanding these conditions and taking proactive steps to protect your skin's health.
Skin Cancer: The Dangerous Invader
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, with over 5 million cases diagnosed each year in the United States alone. It occurs when skin cells undergo abnormal changes and grow out of control, forming a tumor. The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma, with melanoma being the most aggressive and potentially life-threatening form.
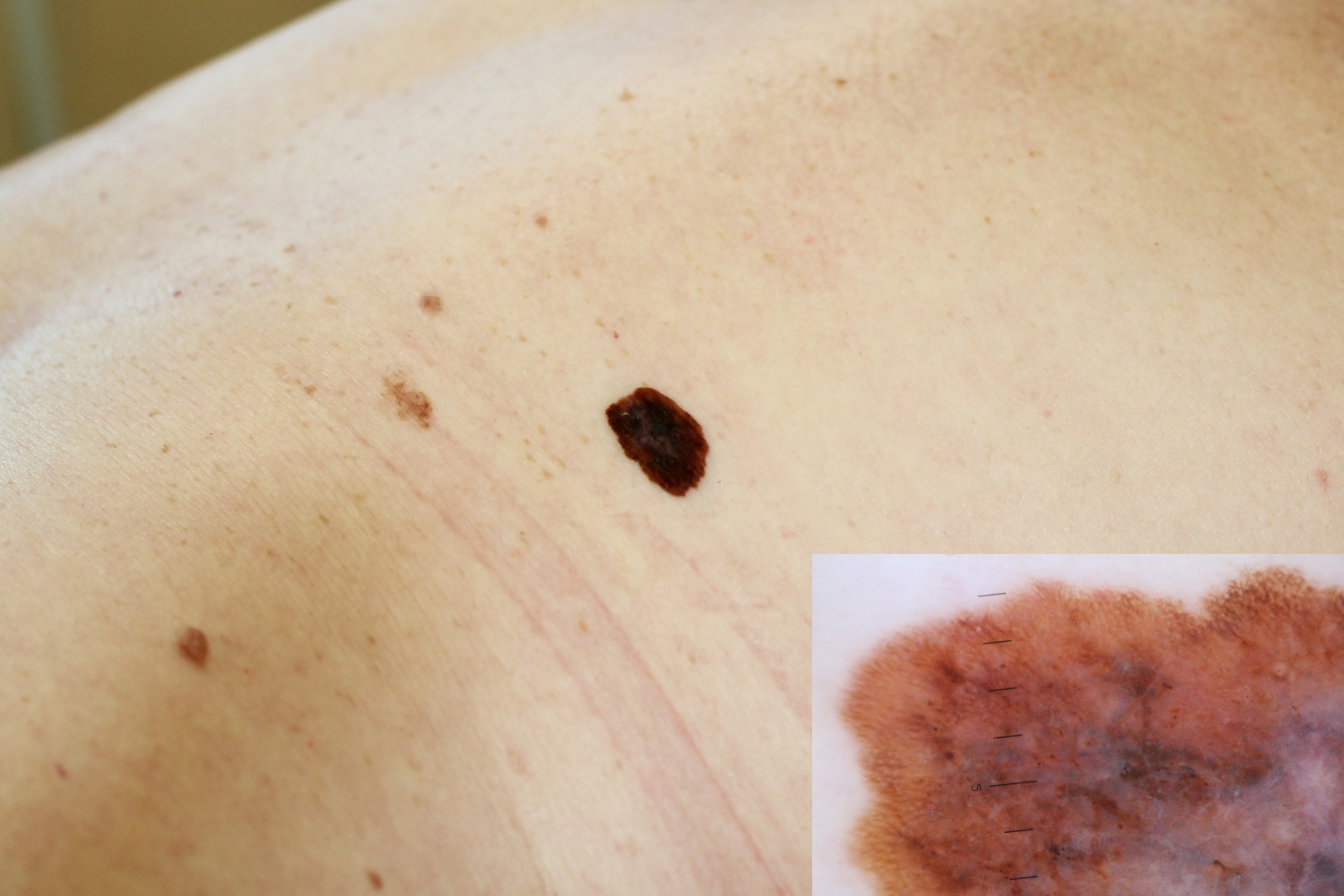
When it comes to identifying skin cancer, it's crucial to look out for the ABCDEs:
A – Asymmetry
One half of the mole or spot does not match the other half.
B – Border
The edges are irregular, blurred, or poorly defined.
C – Color
The color is not uniform and may include shades of brown, black, or even red or blue.
D – Diameter
The spot is larger than 6mm in diameter, about the size of a pencil eraser.
E – Evolution
Changes in size, shape, color, or texture over time.
If you notice any of these warning signs or changes in your skin, it's essential to seek help from a dermatologist promptly. Early detection and treatment are key in successfully managing skin cancer and preventing it from spreading.
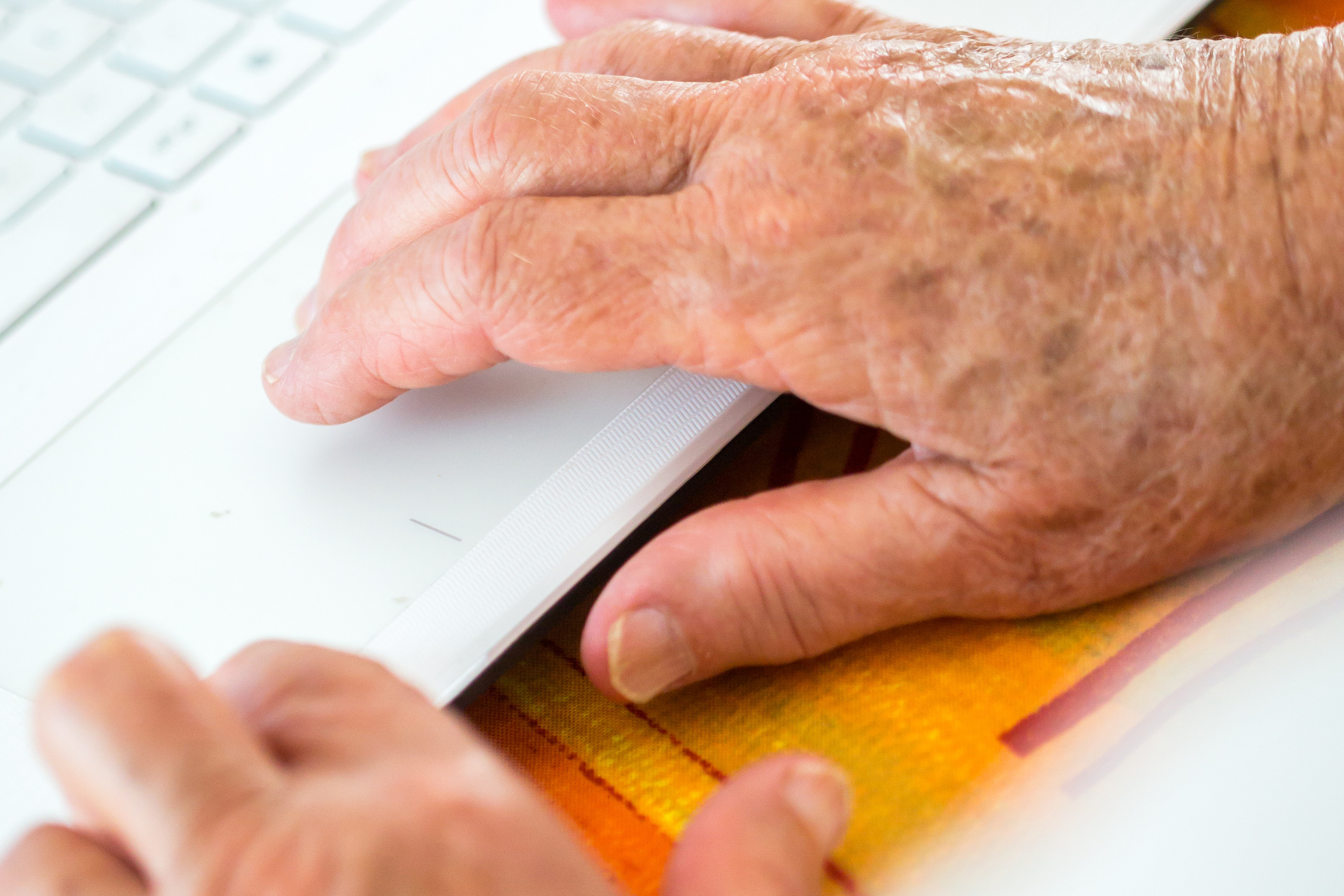
Age Spots: The Harmless Pigment
Age spots, also known as liver spots or sunspots, are flat, brown, or black spots that appear on the skin due to prolonged sun exposure and aging. These spots are typically harmless and more common in older adults, appearing on areas of the skin that receive the most sunlight exposure, such as the face, hands, shoulders, and arms.
Unlike skin cancer, age spots are generally uniform in color and size, without any notable changes over time. They are more of a cosmetic concern than a medical one, although they can sometimes be confused with skin cancer due to their appearance.
Prevention and Protection: Your Skin's Best Defense
Regardless of whether you're dealing with age spots or concerns about skin cancer, protecting your skin from harmful UV rays is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. Here are some tips to help you safeguard your skin's well-being:
1. Wear sunscreen with at least SPF 30 daily, even on cloudy days.
2. Seek shade during peak sunlight hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
3. Wear protective clothing, including hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves.
4. Perform regular skin checks to monitor for any changes or abnormalities.
5. Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet to support overall skin health.
At Fall Creek Skin and Health Clinic, our team of experienced dermatologists and healthcare professionals is dedicated to providing comprehensive care for patients of all ages. Whether you're seeking treatment for skin-related issues like acne, moles, or skin cancer, or need assistance with general practice problems such as allergies or minor illnesses, we're here to support you every step of the way.
Remember, your skin is a reflection of your overall health, so prioritize its well-being by staying informed, vigilant, and proactive in your skincare routine. By understanding the differences between skin cancer and age spots and knowing when to seek help, you can take control of your skin's health and enjoy a lifetime of radiant, healthy skin.