Effective Home Care for Minor Burns and Scalds
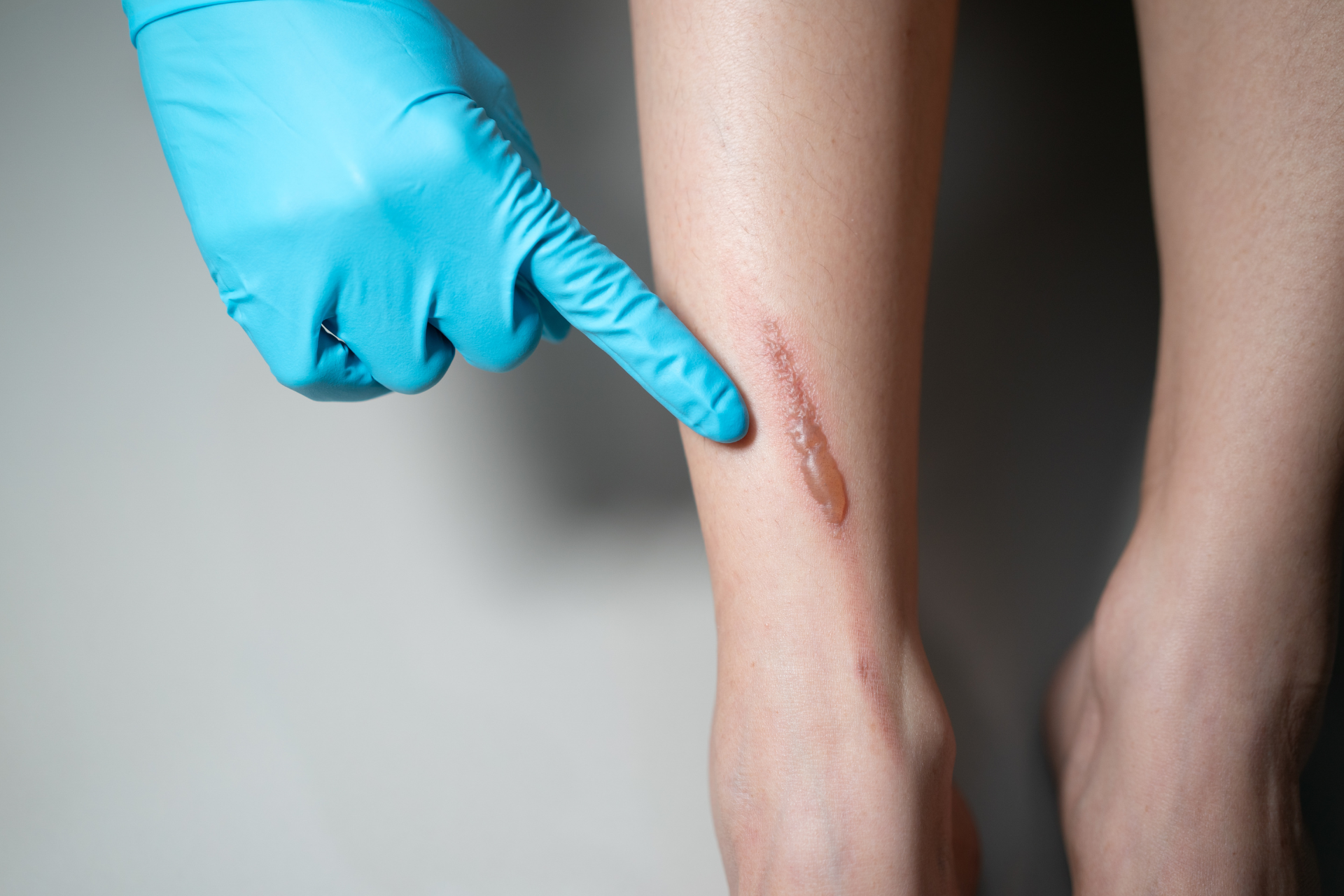
At Fall Creek Skin and Health Clinic, we understand that accidents happen, and minor burns and scalds can be part of everyday life. Whether it's a cooking mishap or an encounter with a hot object, knowing how to manage these injuries at home can make all the difference in recovery. Here, we provide practical steps for effective home care to help soothe and heal minor burns and scalds.
Recognizing the Severity
Before diving into treatment, it’s crucial to assess the severity of the burn or scald. Minor burns typically involve the outer layer of skin (epidermis) and can be classified as first-degree burns. These burns may turn red and cause discomfort but won’t damage the deeper layers of skin. If you experience severe pain, blistering, or the burn covers a large area, seek medical attention at our clinic or call emergency services.
Immediate First Aid
1. Cool the Burn
The first step is to cool the burn. Place the affected area under cool (not cold) running water for about 10 to 20 minutes. If running water isn’t available, a cool compress will suffice. Avoid ice directly on the skin as it can cause further damage. Cooling the area helps reduce pain, swelling, and potential tissue injury.
2. Clean the Area
After cooling, gently clean the burn with mild soap and water. Pat the area dry with a clean cloth. Keeping the burn clean helps prevent infection, a common complication even with minor burns.
3. Apply a Barrier
Once the area is clean and dry, you can apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment (like Neosporin) to the burn. This aids healing and helps reduce the risk of infection. Alternatively, you may also use an aloe vera gel which provides soothing relief and hydration.
Protect and Comfort
4. Cover the Burn
Use a sterile, non-stick bandage or clean cloth to cover the burn. This serves as a protective barrier against dirt and bacteria, promoting healing. Change the dressing daily or whenever it becomes wet or dirty.
5. Pain Relief
If discomfort persists, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be taken, following the recommended dosage instructions. Always consult your healthcare provider if you have any concerns or pre-existing conditions.
Monitoring Recovery
6. Watch for Signs of Infection
While minor burns and scalds usually heal well, it’s essential to monitor for signs of infection. Look for increased redness, swelling, or pus formation. If you experience fever, chills, or worsening pain, consult with us at Fall Creek Skin and Health Clinic.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many minor burns can be managed at home, understanding when to seek professional advice is vital. If the burn covers a large area, is located on the face, hands, feet, or over a major joint, or if you have any accompanying symptoms like difficulty breathing, contact our clinic immediately. Our experienced team is here to provide the necessary care.
Conclusion
At Fall Creek Skin and Health Clinic, we aim to empower our patients with the knowledge and tools to handle everyday injuries effectively. Minor burns and scalds can be painful, but with the right home care techniques, you can minimize discomfort and promote speedy recovery. For persistent or severe cases, don’t hesitate to reach out; we’re here for you every step of the way!