Cryosurgery vs. LEEP: Comparing Two Common Treatments for Precancerous Conditions
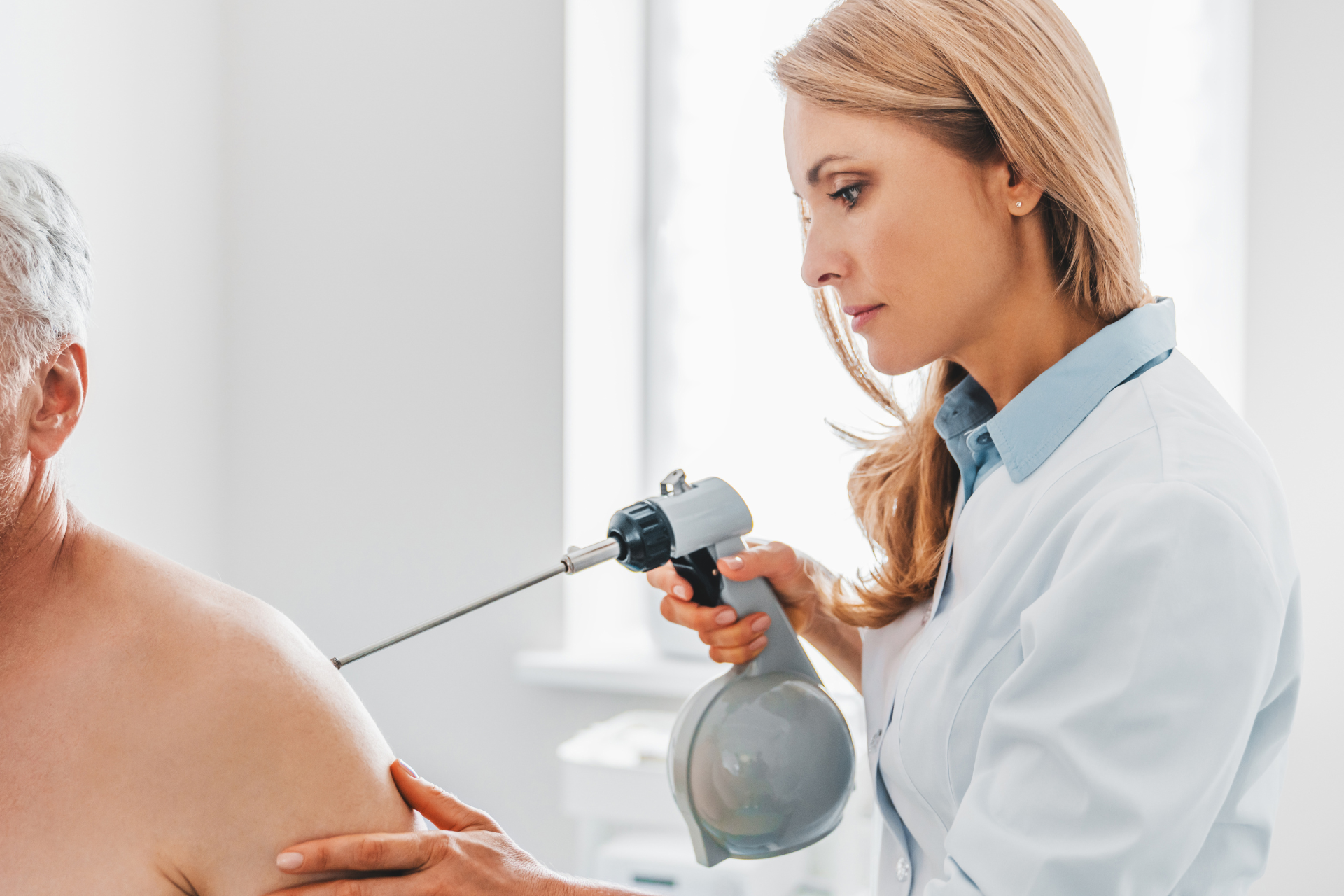

At Fall Creek Skin and Health Clinic, we understand the importance of getting timely and effective treatments for any precancerous conditions that may arise. Among the options available, cryosurgery and Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP) are two commonly discussed treatments. Both methods aim to remove abnormal cells, but they operate through different mechanisms and are suitable for various types of conditions. In this post, we will explore each procedure, their benefits, potential risks, and when they may be recommended.
What is Cryosurgery?
Cryosurgery involves the application of extreme cold to destroy abnormal tissue. Typically, liquid nitrogen or argon gas is used to freeze the targeted area, allowing the body’s immune system to clear away the dead cells. This outpatient procedure is frequently employed to treat skin lesions, warts, and precancerous skin conditions such as actinic keratosis.
Benefits of Cryosurgery
One of the primary advantages of cryosurgery is its minimally invasive nature. It requires little to no anesthesia, and most patients can return to their daily activities almost immediately after the treatment. Additionally, cryosurgery generally results in minimal scarring, making it a preferable option for those concerned about aesthetic outcomes. Because it can be performed quickly in the office, it’s also a time-efficient choice for patients.
Risks of Cryosurgery
While cryosurgery is largely safe, it is not without potential drawbacks. Patients may experience swelling, blistering, or redness in the treated area. There is also a risk of hypopigmentation, where the skin may lose color in the affected area post-treatment. It's essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine if cryosurgery is suitable for your specific condition.
What is LEEP?
LEEP, or Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure, is a technique that uses a thin wire loop heated by electric current to remove abnormal cervical tissue. It is commonly used for the treatment of cervical dysplasia, which refers to precancerous changes in cells on the cervix. Unlike cryosurgery, LEEP is often performed in a specialized medical setting and may require local anesthesia.
Benefits of LEEP
The primary advantage of LEEP is its precision. The procedure allows for not just the removal of abnormal tissue but also provides a clear view, enabling pathologists to analyze the excised tissue for cancerous changes. This diagnostic capability is a critical factor for monitoring any recurrent or progressive disease. Additionally, LEEP has a higher success rate for completely excising lesions compared to cryosurgery.
Risks of LEEP
As with any procedure, LEEP comes with potential risks. Patients may experience bleeding, infection, or cramping following the procedure. There is also a possibility of cervical stenosis, a condition where the cervix narrows. Women who may want to become pregnant in the future should discuss potential implications with their healthcare provider.
Conclusion
When comparing cryosurgery and LEEP, it’s clear that both treatments have their unique benefits and considerations. Cryosurgery is excellent for superficial skin conditions, while LEEP is more suitable for cervical dysplasia. At Fall Creek Skin and Health Clinic, our experienced team is dedicated to helping you make an informed decision about your treatment options. If you have concerns about precancerous conditions or wish to explore these procedures further, we encourage you to schedule a consultation. Your health and well-being are our top priorities, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.

Need Our Services?
Book a free consultation

Our promise is to offer high-quality medical attention at a fair price in a clean, friendly, and professional environment.
QUICK LINKS
BUSINESS HOURS
- Mon - Thu
- -
- Friday
- -
- Saturday
- Appointment Only
- Sunday
- Closed
All Rights Reserved | Fall Creek Skin and Health Clinic |
